In-vitro fertilisation
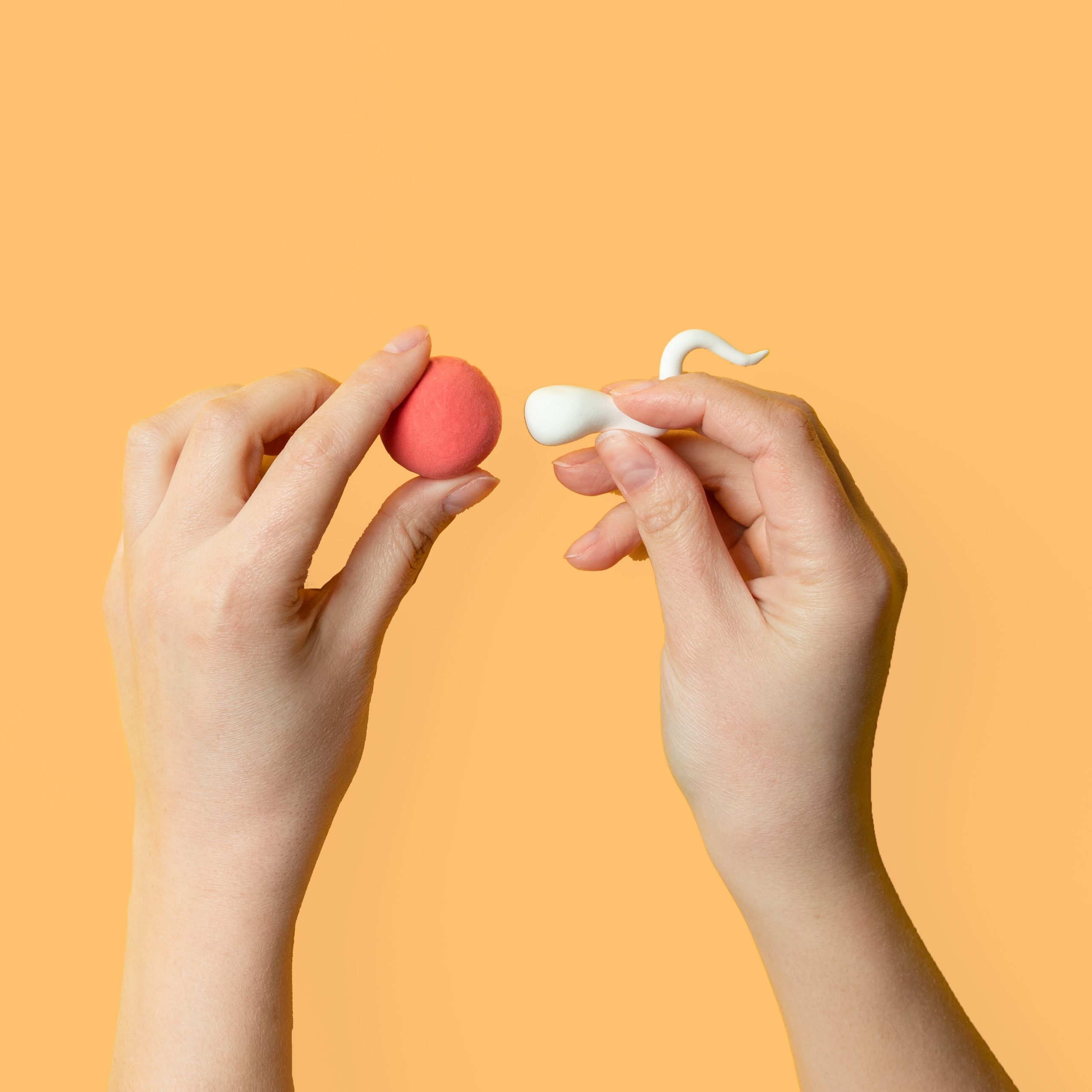

What is in-vitro fertilization (IVF)?
In-vitro fertilization is also commonly known as IVF (from its initials).
Consists of the fertilization of an egg with sperm in a laboratory. The fertilized egg is then cultivated in the laboratory to obtain an embryo, which will then be transferred to the uterus of the future mother.
The cells can be combined using conventional IVF or by way of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
When is In-vitro fertilization indicated?
In-vitro fertilization or IVF is indicated in the following cases:
Women with obstructed fallopian tubes.
Couples with severe male factor.
Ovulation disorders.
Women with limited egg reserve.
Couples that have not achieved pregnancy through other simpler techniques.
Sterility of an unknown origin.
Endometriosis.
Pregnancy rate of In-vitro fertilization
Clinical pregnancy rate detecting a heart beat:
Women under 38 years of age
%
Gestation rate per cycle
%
Clinical gestation (with a heartbeat present)
(average age of 41)
%
Gestation rate per cycle
%
Clinical gestation (detection of a heartbeat)
%
Gestation rate per cycle
%
Clinical gestation (with a heartbeat present)
%
Gestation rate per cycle
%
Clinical gestation (detection of a heartbeat)
Age is a determining factor in assisted reproduction treatment. If you are using your own eggs and you are under 38 years old our success rate is 57% in the first cycle. If you are over 38 years old our success rate is 21% in the first cycle. It is important to note that the chances of getting pregnant are cumulative, that is, they increase with each attempt (the maximum number of attempts that we recommend in our fertility clinic is 3).
By clinical pregnancy * it is understood as the detection of a foetal heartbeat on an ultrasound scan.
Technique for in-vitro fertilization
- 1. Ovarian stimulation.
- 2. Egg retrieval (ovarium puncture).
- 3. Fertilization in the laboratory.
- 4. Embryo culture.
- 5. Embryo transfer.
- 6. Vitrification of the unused embryos.
- 7. Pregnancy test.
- 8. The ultrasound.

Normally, a single egg is produced during a woman’s natural cycle. Ovarian stimulation consists of administering hormones by subcutaneous injection to obtain more eggs. The entire process is monitored by a series of ultrasound scans, for which our specialists are available seven days a week to do. Depending on the type of protocol used and the rapid response of the ovary, the duration of the process will vary between 10 and 12 days.
Once the follicles reach the appropriate size and number, a hormone called HCG is administered to complete the maturation of the eggs. Approximately 36 hours after administering the HCG, the mature eggs can be aspirated from the ovary.

This procedure consists of the aspiration of the mature oocytes using ultrasound guidance and administrating a gentle sedation to the patient so that she does not feel any type of discomfort. This minor procedure usually takes about 15 minutes.
On the day of this procedure it is recommended not to carry out activities in which you need to be fully alert, such as driving, or activities that require a lot of effort, even though you may feel perfectly well, it is advisable to just relax and take it easy.

Once the eggs have been obtained, they are inseminated with the partner’s semen which has been previously prepared in the laboratory.
Spermatozoid selection can be carried out using a technique called MACS, immunomagnetic selection of the spermatozoid with the greatest capacity to fertilise the egg, or using conventional capture methods.
Fertilisation can be carried out by classical IVF, for this the biologist places each oocyte in contact with some 25 to 50,000 previously selected spermatozoids, and lets fertilization occur unaided.
Alternatively ICSI may be used, which consists of introducing a single sperm into the cytoplasm of the ovule by puncturing it with a fine pipette. This latter technique is used mostly in cases of severe spermatozoid disorders, poor oocyte quality, valuable or scarce eggs, elderly women, suspicion of low fertilisation rate or prior failures using classic IVF treatments.
TESE is an ICSI technique using spermatozoids obtained via testicular biopsy. It is recommended when there are no spermatozoids in the ejaculation (azoospermia) though they are present in the testicles, or when ejaculation causes serious damage to the spermatozoids.
The embryos are cultured and monitored in the laboratory for several days (from 2 to 6). For this, we use modern incubation techniques to monitor its evolution in real time (morphokinetics). We have incubators equipped with time lapse technology, which incorporates an image capture system, which allows us to observe the embryos development from their fertilization until the moment of transfer to the uterus, without having to remove them from the incubator. In this way, the culture conditions are more stable, which means an improvement in embryo quality. In addition, this technology facilitates the selection of the best embryos to transfer and freeze.

This consists of the introduction of the embryos inside the uterine cavity. To do this, a speculum is placed in the vagina and a fine cannula is inserted that carries the embryos which are deposited in the uterus under ultrasound guidance. This process is quick and painless.
After the transfer we recommend relative bed rest during the rest of the day and the following day, after which the woman can return to her usual activities.
Our only recommendation is to avoid vigorous physical activities and sports during the two weeks after the transfer. Travelling and driving are not seen as a problem.
Once the transfer has been carried out, the rest of the good quality embryos are preserved in liquid nitrogen in order to be used in subsequent cycles without the need to carry out the entire process again.
Currently, in the laboratory here at Clinica Fertia we use the Vitrification or ultra-fast freezing technique.
12 days after the embryo transfer, a BHCG (pregnancy) test will be done to confirm the pregnancy.
Alternatively a urine test can also be done 14 days after the embryo transfer.
Until the pregnancy is confirmed, the medication prescribed on the day of the embryo transfer should be continued.

15 days after the BHCG analysis, an ultrasound is performed to confirm the number of embryos that have implanted (embryo sac stage) and the presence of a heartbeat
It is recommended that the hormone substitute is maintained at least until the tenth week of pregnancy.
Frequently asked questions about reproduction treatments
If you would like more information about our treatments, we are always available to help and answer any of your questions.
How long do I have to wait to start treatment?
How many attempts can I make?
In the case of artificial insemination, here at the clinic we recommend a maximum of four attempts, since 90% of pregnancies occur in the first four cycles.
Regarding In-vitro fertilisation or microinjection, our clinic never makes more than four attempts using these techniques.
In the case of egg donation, it is more difficult to establish a limit, this will normally be determined by psychological and also economic factors.
Can you use these techniques when you have already entered menopause?
In these cases, the reception of eggs from a donor must be used.
What are the biggest concerns of egg or sperm recipient couples?
Another factor that concerns a couple is the health of the donors and the physical resemblance to them.
In our centre, both in the case of sperm donors and egg donors, our goal is to seek that the physical resemblance is as similar as possible to the parents.
Are these treatments expensive?
Clínica Fertia is a pioneer in maintaining an honest and transparent policy. Since 2002 we have published the information of the cost of our treatments on our website.
Treatment Price
Patients who come to Fertia are informed from the very first moment with complete transparency about the cost of our treatments.
If you have any questions, consult our team.
In-vitro fertilisation |
|
Treatment includes: First Visit Oocyte retrieval Fertilisation Embryo culture Embryo transfer Ultrasounds |
€4,195 |
In-vitro fertilisation using a male donor |
|
Treatment includes: First Visit Oocyte retrieval Donor sample Fertilisation Embryo culture Embryo Transfer Ultrasounds |
€4,595 |